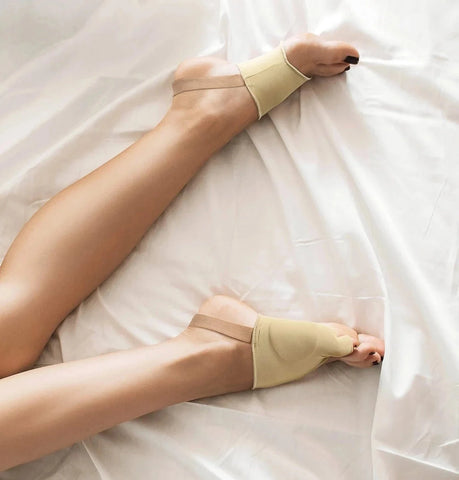
If you have any of the following symptoms, you may have a bunion problem:
• Pain or soreness around the big toe joint
• Redness or swelling around the big toe joint
• Difficulty moving the big toe
• A bump at the base of the big toe
• Thickening of the skin around the big toe
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor or podiatrist to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Your doctor may recommend some lifestyle changes such as wearing wide-toed shoes, avoiding high heels and pointy-toed shoes, and using an orthopedic bunion sleeve to cushion the affected area. They may also suggest stretching and strengthening exercises for the feet and ankles.
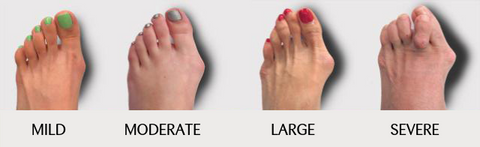
A bunion, known technically as hallux valgus, is a bony bump on the side of the foot at the base of the big toe. Bunions develop slowly as pressure on the joint at the base of the big toe causes the toe to move out of place, leaning inward toward the second toe.
Because this joint carries a lot of weight during activities like standing and walking, bunions can cause foot pain, stiffness, redness, and swelling. Calluses may form where the big toe and second toe rub together or on the ball of the foot. Unless they are treated, bunions get worse over time, and it may become difficult to wear regular shoes or walk without pain. Bunions can occur in one or both feet.


Risk factors
These factors might increase your risk of bunions:
- High heels. Wearing high heels forces your toes into the front of your shoes, often crowding your toes.
- Ill-fitting shoes. People who wear shoes that are too tight, too narrow or too pointed are more likely to develop bunions.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Having this inflammatory condition can make you more likely to develop bunions.
- Heredity. The tendency to develop bunions might be the result of an inherited problem with the structure or anatomy of your foot.
Complications
Possible complications of bunions include:
- Bursitis. This painful condition occurs when the small fluid-filled pads that cushion the bones near your joints become inflamed.
- Hammertoe. An abnormal bend that occurs in the middle joint of a toe, usually the toe next to your big toe, can cause pain and pressure.
- Metatarsalgia. This condition causes pain and swelling in the ball of your foot.
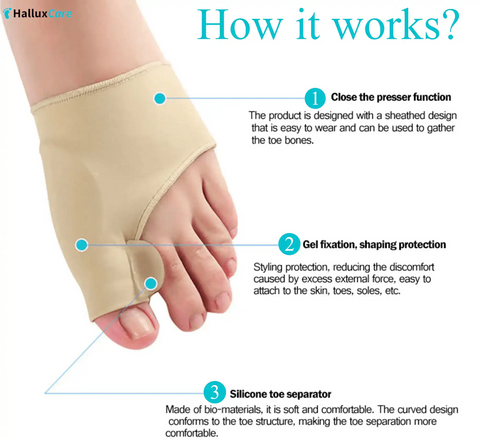
Non - Surgical Treatments
Best non-surgical treatments that will relieve the pain and pressure of a bunion include:
- Changing shoes. When you can wear roomy, comfortable shoes that provide plenty of space for your toes. Avoid Ill-fitting shoes.
- Maintaining your weight. Getting at least 30 minutes of exercise daily and having a balanced diet will maintain a healthy lower weight, reducing the amount of pressure against your feet and the bunion.
- Orthopedic Bunion Pain Relief & Correction Sleeves. One of the most effective & podiatrist-recommended ways to treat bunions are medical-grade bunion sleeves with protective gel pads. They are specifically designed by professionals, in consultation with podiatric surgeons to stop the bunion from progressing to worse stages and eliminate daily swelling, chronic pain and inflammation. Learn More
What also can help:
- Medications. Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve) can help you control the pain of a bunion. Cortisone injections also might help.
- Applying ice. Icing your bunion after you've been on your feet too long or if it becomes inflamed can help relieve soreness and swelling. If you have reduced feeling or circulation problems with your feet, check with your doctor first before applying ice.